Working with Slicers and Filters
Slicers vs. Filters

In Power BI, both slicers and filters allow you to select and exclude data, but they have some key differences.
- Slicers live directly on the report canvas alongside other visualizations, giving you finer control over the data you see.
- Filters always appear together on the filter pane. Filters can apply to every visualization in a page or report, or a single visual, while slicers can be designed to apply to a custom group of objects.
Slicers
Slicers can take different forms and appear anywhere in a report. They usually take the form of a dropdown menu or simple buttons that you can toggle. Slicers can be designed to exclude data you don't want to see or change the data dimensions displayed by certain visuals.
Filters
Filters restrict the data displayed in Power BI reports and can be tied to specific dimensions or measures. They offer advanced ways to filter data, such as top N and relative date filtering. Filters can have different scopes, limiting data in visuals on a single page, the entire report, or even just a single visual.
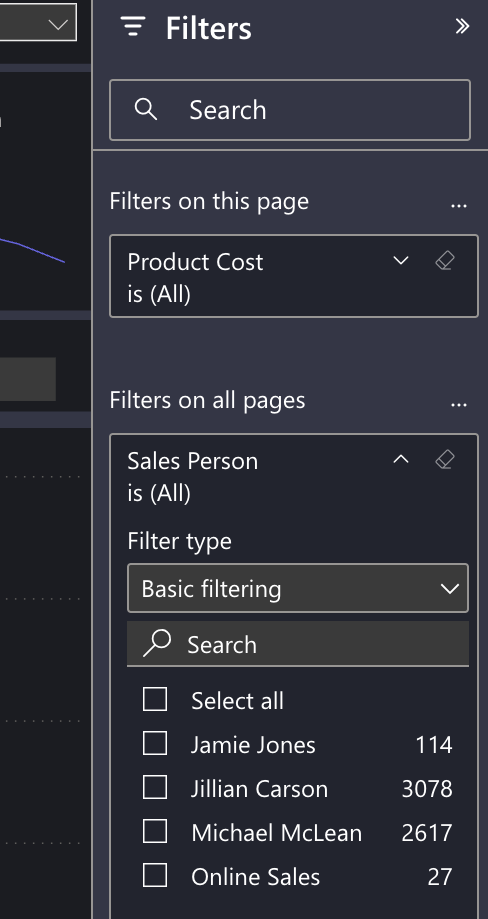
Report, Page & Visual Filters
It's important to understanding the scope of filters in Power BI. Some filters limit data in visuals on a single page, while others impact the data displayed on all pages of a report. Occasionally, you may encounter a filter with an even narrower scope—a filter that impacts data only for a single visual.
Filter Types
The two most common types of Power BI filters are Basic Filtering and Advanced Filtering. Date fields offer a third type of filter called Relative Filtering.
Basic filters
Basic filtering provides a checklist where you can include and exclude values one at a time, similar to Microsoft Excel.
Advanced filters
Advanced filtering allows you to set complex rules to filter a field using options like "contains," "starts with," "is greater than," and "is not."
Relative date filters
Power BI offers advanced filtering options for date and time fields. You can select a date and time from the calendar picker and specify rules such as "is on or after" or "is not." Additionally, you can use Relative Date and Relative Time filters to show data relative to today's date or specific hours and minutes.
